
If you have a garden at your lake house, you’re probably familiar with the Plant Hardiness Zones. Designed by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, this guide separates the country into zones based on average annual minimum winter temperature. Each zone is split by 10 degrees and has its unique features, such as the first and last frost date and length of seasons. This helpful tool clarifies which plants will thrive in your garden. For example, if you’re a gardener in zones 1-3, the Plant Hardiness Zones will warn you against planting a peach tree in your garden, which wouldn’t flourish outside the southernmost zones.
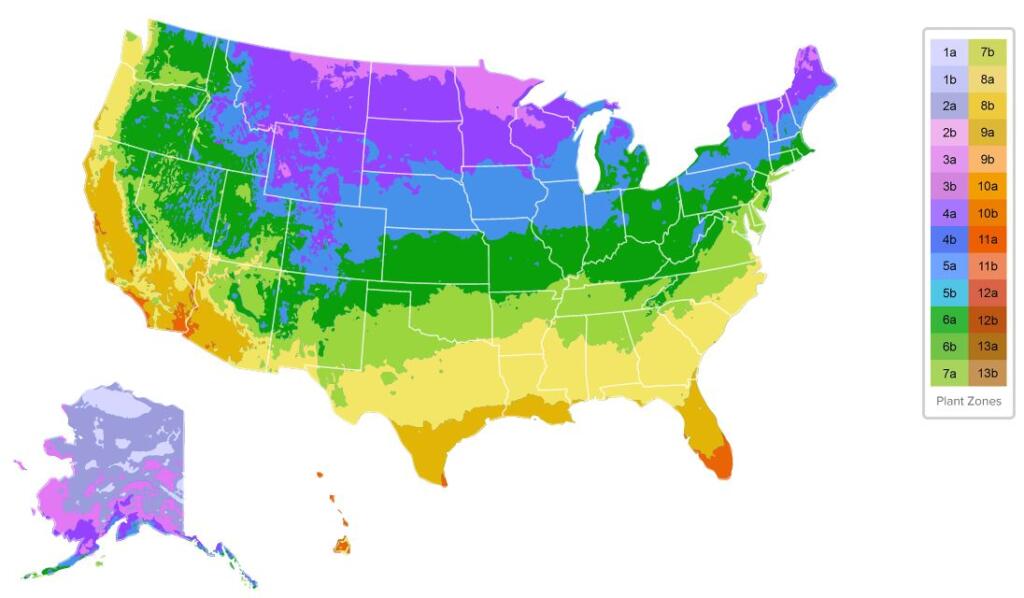
If you’ve been browsing the Lake Homes blog in the last few months, you may have caught the first two articles in our series on gardening zones. While the first two covered zones 7-9 and zones 4-6, we’re now turning the spotlight on the coldest areas of the U.S. — zones 1-3.
Region Characteristics

In zones 1-3, the average annual minimum temperature is between -60 degrees and -30 degrees Fahrenheit with zone 1 being the coldest. Most of zone 1 is located in Alaska, where the tundra climate can be especially harsh for gardening. In zones 2 and 3, which include the northernmost United States and high altitude areas, these low temperatures also present a challenge for gardeners. Due to the unforgiving weather, it’s crucial to consult the Plant Hardiness Zones to determine which plants are most likely to survive the winter in your garden. Aside from temperature, these regions also tend to have low moisture and high winds, creating more barriers to plant survival.
Main Takeaways
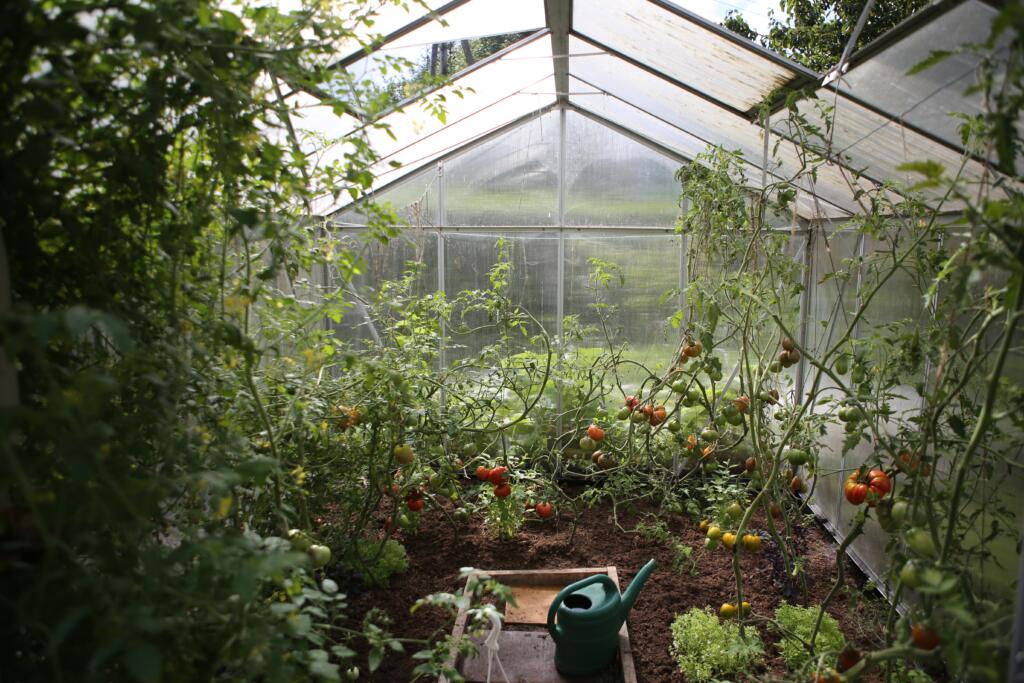

Due to the harsh features of these regions, northern gardeners’ planting window is shorter than those in other zones. Kevin Espiritu, the founder of Epic Gardening, clarifies, “Gardeners in zones 1-3 have about 2 months to plant, and that’s it.” If you’re living in these zones, it’s crucial to take advantage of this brief time. Luckily, certain types of gardening can help. Scott Fanello, a writer for Total Gardener, advises those in zones 1-3 to master cold-frame gardening. With this simple structure that utilizes insulation and solar energy, you can create a microclimate for your plants. He also recommends building a greenhouse at your lake home if you have the money and time. Despite these challenges, life in zones 1-3 isn’t all bad. Espiritu notes that one advantage to growing plants in Alaska is their long summers (almost 20 hours per day of sunlight), causing gardeners in this region to break records in terms of large vegetables.
Plants to Pick

Due to the harsh weather conditions, the best plants to choose in zones 1-3 are tough ones that can survive droughts. It’s also best to select native plants that are already adapted to the climate. Thankfully, several plants are hardy enough to thrive in this cold, dry weather. Nikki McAteer, marketing director of Perfect Plants Nursery, comments, “Only a handful of perennial plants will grow outside and come back year after year. Planting annuals is a great solution to these punishing temperatures.”
In contrast to perennials that need more maintenance, annuals are less of a commitment. Most vegetables are grown as annuals, so plants like beans, broccoli, potatoes, and tomatoes have a good chance of survival in zones 1-3. Fanello recommends focusing on fast-growing annuals in particular. Some examples include salad greens and herbs like basil, oregano, and rosemary. Overall, it’s helpful to pick plants with a short growing season so they’ll mature and be ready for harvest in the 2-month window that these zones offer.
Despite the harsh weather in zones 1-3, northern gardeners are quite savvy when it comes to working with what they have. If you own a lake house in these zones, we hope these tips help your garden flourish. It’s also a great idea to connect with other gardeners in your zone through meetups, Facebook groups, and local farmer’s markets. Plus, with all the available vegetable options in these northern zones, you’ll always have something to add to your homemade salad!

